设计模式笔记
本文最后更新于:2025年12月2日 晚上
Design Pattern
0. Overview
设计模式介绍
- 经过证明、可复用的解决方案
- 针对软件中的重复出现问题
四个重要组成部分
- Pattern Name
- Problem
- Solution
- Consequence
1. UML
Unified Modeling Language
Overview of UML
为什么需要UML
- 帮助以OO思想进行高效、正确的编程
- 让开发、客户、架构师拥有共同的语言
- 呈现big picture
最大价值:Visual Modeling
- UML以半形式化
- 图可以表达流程、交互、顺序、关系
UNL的三个基本概念
- UML是通用建模语言
- 用图形和文本来描述软件系统
- 汇集各种建模方法的最佳实践
Structure of UML
-
Use-case View 用户视图
- 从用户视角描述系统
- 整个系统的核心
- 用例图体现需求
-
Structural View 结构视图
- 系统的静态结构
- 包含:类、对象、包、组件
-
Behavioral View 行为视图
- 描述对象之间交互
- 顺序图、状态图
-
Implementation View 实现视图
- 逻辑组件关系
-
Deployment View 环境视图
- 系统部署结构
- 服务器、硬件节点
UML图分两类
结构图(关注“系统是什么”)
- 类图(Class Diagram
- 对象图、包图、组件图、部署图等
行为图(关注“系统怎么动”)
- 用例图、顺序图、活动图、状态图等
Class Diagram
类图展示:类、属性、操作、类之间关系
类图的职责:
属性 -> 数据职责
操作 -> 行为职责
类图描述 static structure
类图三大组成
-
类名
- 首字母大写
- 避免缩写
-
属性
- [Access] Name: Type = Default
- Camel case naming 驼峰命名法
-
操作
-
[Access] functionName([argument]) : return type
-
首字母小写
-
动词开头
-
类之间的关系
Association (关联)
两个类之间有关系、有引用、有联系
最普遍的关系、UML表示为一条实线
- Multiplicity (多重性)
展示关联关系中的数量关系
| 表示法 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 恰好一个 |
| 0…1 | 可有可无 |
| * | 多个 |
| 1…* | 至少一个 |
| 0…* | 可以没有,也可以很多 |
- Aggregation (聚合性)
整体-部分关系,部分可以脱离整体
空心菱形 ⭘——— 线 ——> 部分
弱的整体关系
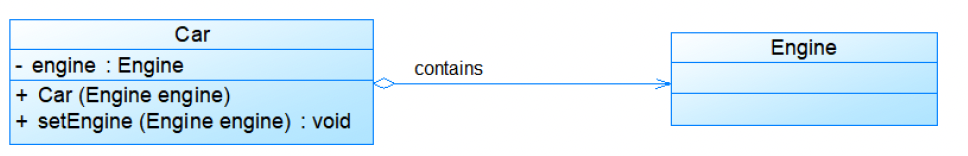
汽车可以包含一个发动机,发动机也可以单独存在
Composition (组合)
强整体关系,部分不能脱离整体
实心菱形 ◆—— 线 ——> 部分
区别总结: 聚合:整体和部分可以分离 组合:部分生命周期由整体控制(整体消失,部分必消失)
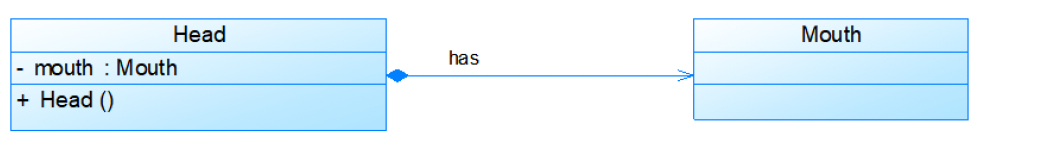
头包含一个嘴,嘴不能单独存在
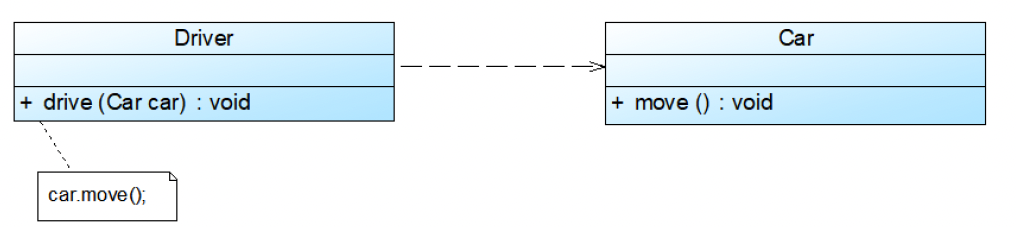
Dependency (依赖)
依赖是最弱的关系,通常发生在:
- 方法参数类型
- 方法内部临时使用的对象
- 静态方法调用
UML 表示:
- 虚线箭头 ——→
含义: A 依赖 B = A 使用到 B,但不拥有 B。
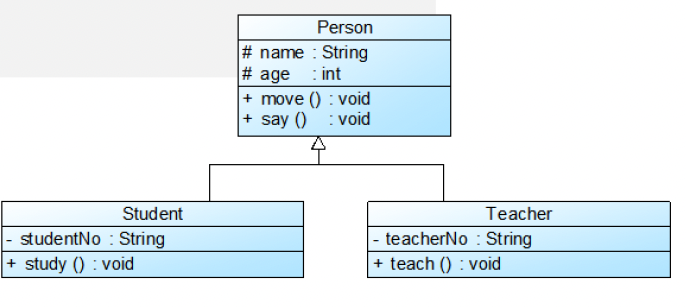
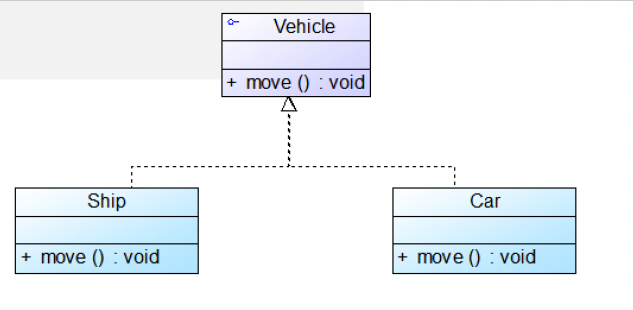
Generalization (泛化)
经典的 OO 概念: 父类 —— 子类
UML 表示:
- 空心三角形箭头 ▼—— 指向父类
Realization (实现)
接口关系:class implements interface
UML 表示:
- 虚线 + 空心三角形 ——▷
2. Principle of OOP
为什么OO
- Maintainability
- Reusability
OO 七大设计原则
| 序号 | 原则 | 核心思想 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 单一职责 SRP | 一个类只做一件事 |
| 2 | 开闭原则 OCP | 对扩展开放,对修改关闭 |
| 3 | 里氏替换 LSP | 子类必须能替换父类 |
| 4 | 依赖倒置 DIP | 面向接口编程,而不是面向实现 |
| 5 | 接口隔离 ISP | 不要给类强行塞无关方法 |
| 6 | 组合复用原则 CRP | 优先使用组合,而不是继承 |
| 7 | 迪米特法则 LoD | 减少对象之间的耦合 |
Single Responsibility Principal
定义:There should never be more than one reason for a class to be changed
High cohesion, low coupling
Open-Closed Principle
软件实体应该对扩展开放,对修改封闭。
Open for extension, but closed for modification.
Liskov Substitution Principle
子类必须能够替代父类的出现
Functions that use pointers or references to base classes must be able to use objects of derived classes without knowing it.
Dependency Inversion Principle
Program to an interface, not an implementation
高层模块不应该依赖低层模块,两者都应该依赖于抽象
抽象不应该依赖细节,细节应该依赖抽象
Interface Segregation Principle
Clients should not be forced to depend upon interfaces that they do not use.
一个类绝不能被迫实现它不需要的方法。 避免臃肿的接口(fat interface)
Composite Reuse Principle
Composition over Inheritance
Law of Demeter
Each unit should only talk to its friends; don’t talk to strangers
一个对象应该尽可能少地了解其他对象。 不要和不必要的对象产生直接联系。
- 不必要通信的对象,永远不要耦合
- 两个对象必要通信,也应该减少直接依赖
- 引入中间类减少耦合
Creational 设计模式
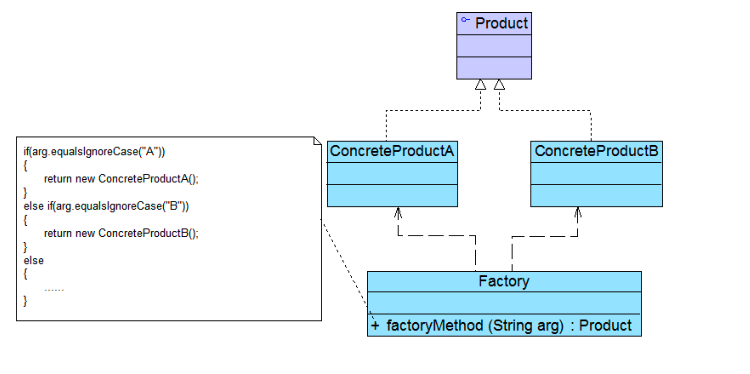
4.Simple Factory Pattern 简单工厂模式 🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟
设计意图:
- 创建对象使用统一接口类型(符合Dependence inversion Principle)
简单工厂:
- Static
- 属于类创建模式
- 根据不同参数返回不同类的实例
- 工厂专门负责创建同类产品
类图
代码
1 | |
优缺点:
- Decouple use & creation
- Client hides product classes
- Flexible with config extension
- factory class is heavy
- 每新增一个产品,需要修改工厂 -> 违反开闭原则
- Hard to extend
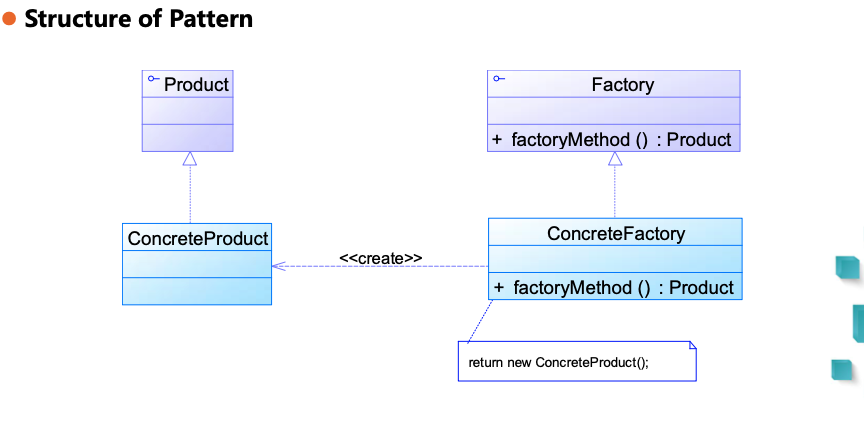
5. Factory Method Pattern 工厂方法 🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟
动机:解决简单工厂违背开闭原则
- 定义一个创建对象的接口,让子类决定创建哪个对象
- 返回共同的接口类型(符合依赖倒置)
类图
代码
1 | |
优缺点
- 隐藏产品创建细节
- 工厂子类独立决定产品类型
- 符合OCP
- 符合DIP
- 类数量成倍增长
- 抽象层次变多,增加理解难度
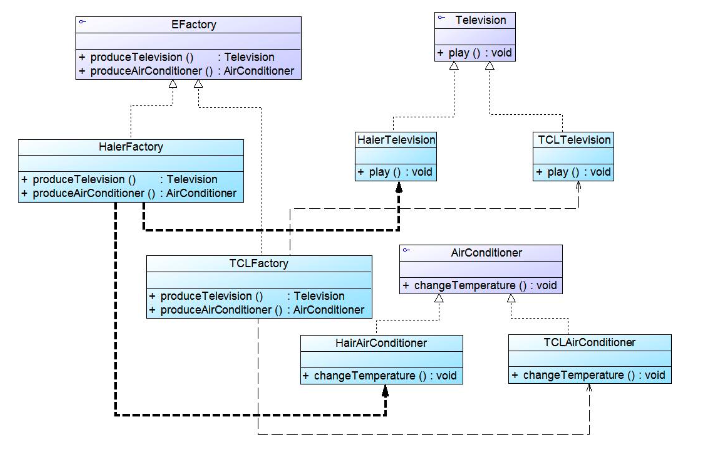
6. Abstract Factory Pattern 抽象工厂模式 🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟
Abstract Factory offer an interface for creating a family of related objects without specifying their concrete classes.
产品族:多品牌 -> 多个产品(电视 + 空调 + 冰箱)
multiple sets of products from multiple producers
类图
实例:
1 | |
优缺点
- Isolation of Concrete Class Generation
- Consistent Interaction within Product Family
- Easy to Add new Product families
涉及的设计模式
- 符合Dependency Inversion Principle
7. Builder Pattern 建造者模式 🌟🌟
对象很复杂,需要分步骤组装完成
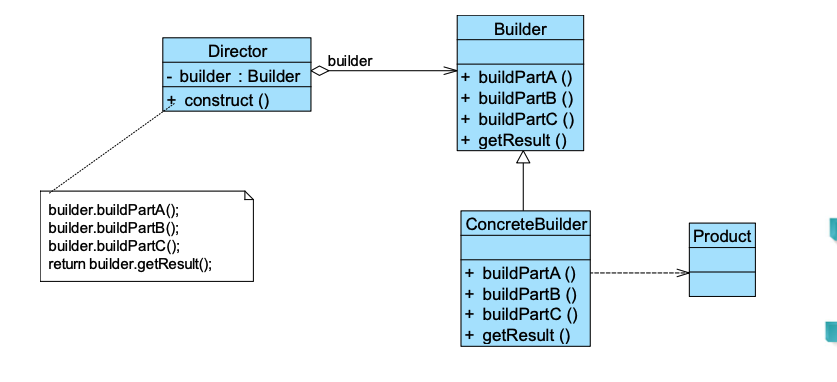
-
Director
-
持有builder
-
只负责控制建造的步骤顺序
-
不关心产品是什么
-
builder.buildPartA(); builder.buildPartB(); builder.buildPartC(); return builder.getResult();1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
2. Builder
- 定义建造步骤
3. ConcreteBuilder
- 实现不同的产品细节
4. Product
``` python
1. 产品类(Product)
class Meal {
String food;
String drink;
public String toString() {
return "Meal: " + food + ", " + drink;
}
}
2. 抽象建造者(Builder)
interface MealBuilder {
void buildFood();
void buildDrink();
Meal getMeal();
}
3. 具体建造者(ConcreteBuilder)
class BurgerComboBuilder implements MealBuilder {
private Meal meal = new Meal();
public void buildFood() { meal.food = "Burger"; }
public void buildDrink() { meal.drink = "Cola"; }
public Meal getMeal() { return meal; }
}
class ChickenComboBuilder implements MealBuilder {
private Meal meal = new Meal();
public void buildFood() { meal.food = "Chicken Roll"; }
public void buildDrink() { meal.drink = "Juice"; }
public Meal getMeal() { return meal; }
}
4. 指挥者(Director)
class KFCWaiter {
private MealBuilder builder;
public void setMealBuilder(MealBuilder builder) { this.builder = builder; }
public Meal construct() {
builder.buildFood();
builder.buildDrink();
return builder.getMeal();
}
}
5. 客户端使用
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
KFCWaiter waiter = new KFCWaiter();
MealBuilder builder = new BurgerComboBuilder();
waiter.setMealBuilder(builder);
Meal meal = waiter.construct();
System.out.println(meal);
}
}
-
设计模式
- 符合Single Responsibility Principle
- 符合Open-Closed Principle
- 符合Composite Pattern
优缺点
- Hide product construction details
- Easy to extend builders
- Precise control of build process
- Not suitable for highly different products
- Too many builders
8. Singleton Pattern 单例模式 🌟🌟🌟🌟
某些对象必须系统全局唯一,并且允许全局访问
Ensure a class has only one instance and provide a global point of access to it. The class is called the singleton class.
三个关键特性
- only has an instance in memory
- accessed by the whole system
- class is responsible for creation
饿汉式
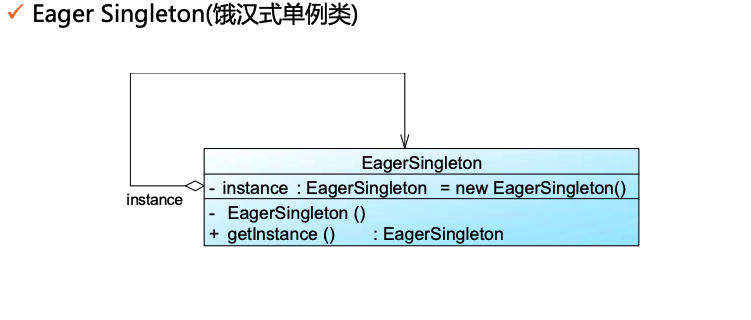
1 | |
懒汉式:Initialization on Demand Holder (IoDH)
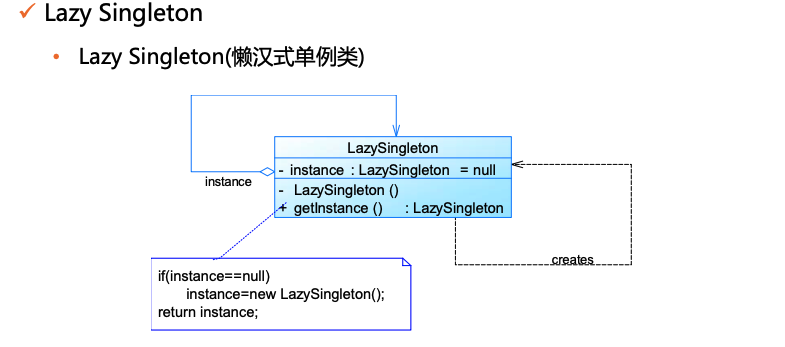
1 | |
优缺点
- Provide controlled access to the unique instance
- Save resources and enhance system performance
- Support multiton variant
- Difficult to extend
- May take too many responsibilities
- Shared state may be lost
8.5. Prototype Pattern 原型模式 🌟🌟🌟
通过复制现有对象,而不是重新new一个来生成新对象
类图
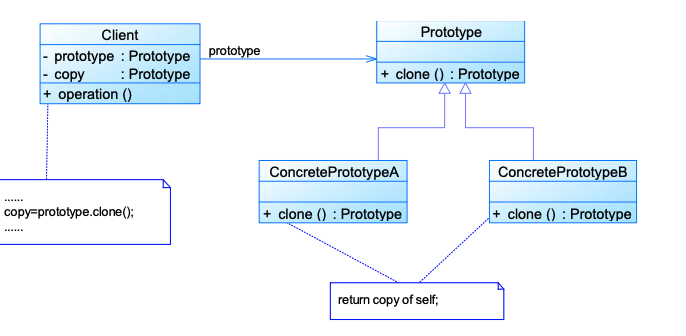
浅克隆:引用类型不复制,只复制引用
类图:
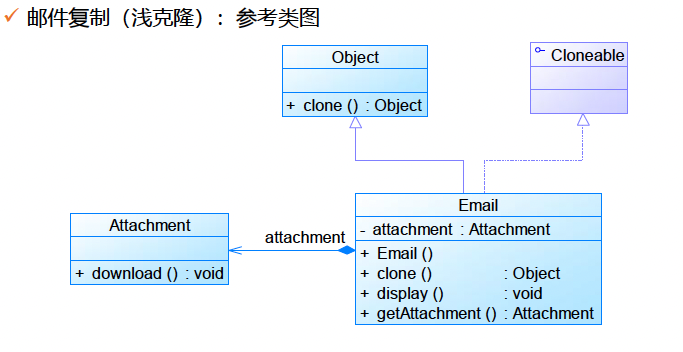
代码
1 | |
深克隆
类图
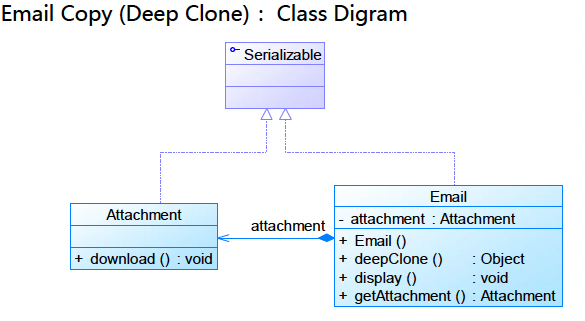
代码
1 | |
优缺点
- Simplifies object creation
- Good extensibility
- Clone method required, 违反Open-Closed Principle
- Hart to modify clones
Structural 设计模式
9 Adapter Pattern 适配器模式 🌟🌟🌟🌟
Adapter Pattern 将一个类的接口转换成客户端期望的另一个接口。使原本因接口不兼容而不能一起工作的类能够协作。
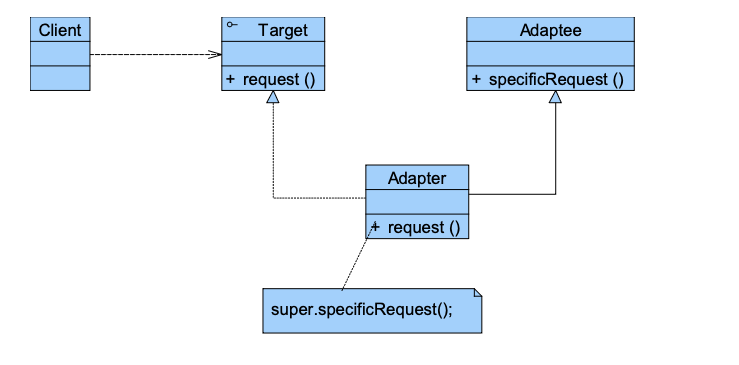
1 | |
-
类适配器通过 “继承(extends)” 获取 Adaptee 行为
-
并通过 “实现(implements)” Target 接口让客户端使用
优缺点
- Decouples Target and Adaptee
- Enhances reusability
- Flexibility and Extensibility
-
Class Adapter Pattern
-
- only one adaptee
- Adaptee classes should not be final classed
- Adaptee can not final
-
Object Adapter Pattern:
- 覆盖Adaptee方法比较麻烦
10. Bridge Pattern 🌟🌟🌟
动机:
将抽象(型号)与实现(颜色)分离,使两者可独立变化。
定义:
- Separates the abstract part from its implementation
- Replaces multiple inheritance with abstract association
- Transforming static inheritance relationships beteen classed into dynamic object composition relationships
抽象类不直接实现功能,而是持有一个“实现类接口”。 两者通过组合建立关系,而不是继承。
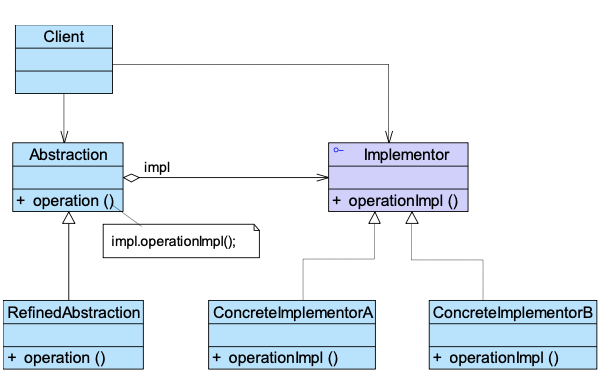
1 | |
优缺点
- Separating the abstract interface and its implementation
- reducing the number of subclassed
- enhance the system scalability
- 符合open-closed principle
- increase the complexity of system
- not easy to understand
11. Composite Pattern 组合模式 🌟🌟🌟🌟
动机:把“整体(容器)”和“部分(叶子)”放在一个统一的结构中操作 —文件夹
定义:将对象组合成树形结构以表示“整体-部分”的层次结构。Composite 模式使得用户对单个对象和组合对象的使用具有一致性。
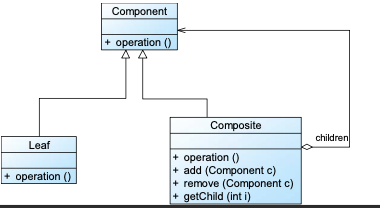
1 | |
优缺点
- Clear hierarchical structure
- uniformly use a composite structure or individual objects
- 符合Open-Closed Principle
- Hard to restrict component types
12. Decorator Pattern 装饰模式 🌟🌟🌟
动机:用继承静态地扩展对象功能,会面临类爆炸,不够灵活;而很多时候我们希望“动态地、按需地”添加功能。
定义:Decorator pattern 动态地为对象添加职责,比继承更灵活,是一种对象结构型模式。
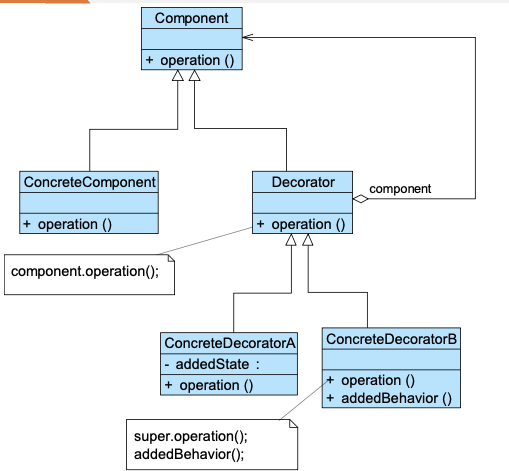
1 | |
优缺点
- More flexible than inheritance
- Runtime dynamic extension
- Multiple decorators support
- Many small objects
- Hard to debug
设计模式
-
符合 Open-Closed Principle
-
符合 Single Responsibility Principle
-
符合 依赖倒置
-
不符合 Interface Segregation Principle
13. Facade 外观模式 🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟
动机:hides the complexities
我们访问网站时: 只记住主页 URL
而不会去记:
- 新闻页面
- 产品介绍页面
- …
- 没有Facade时,client class needs to interact with multiple business clasees. 耦合严重,违背Demeter
- 引入Facade, 客户端只与facade通信
类图
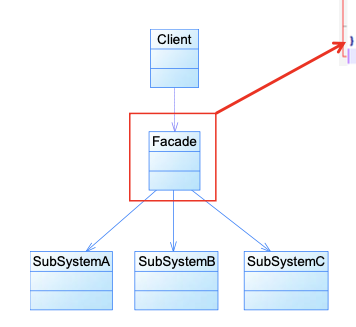
1 | |
优缺点
- 符合Law of Demeter
- Reduce the number of objects the client
- Loose coupling via facade
- New subsystem require modifying facade, 可能违背Open-Closed Principle
相关设计模式
- 符合 Law of Demeter
- 符合 Dependence Inversion Principle: 客户端依赖 "Facade"抽象,不直接依赖子系统
- 可能违背:Open-Closed Principle
Behavioral
14. Chain of Responsibility 职责链模式 🌟🌟
动机:① 事件发起者(Sender)不知道处理者(Receiver)是谁
例如:
- 学生提交奖学金申请
- 学生不知道具体是辅导员、系主任、院长还是校长处理
- 规则由学校内部决定,学生无需了解
② 请求需要按顺序逐级传递
示例链路(P4):
辅导员 → 系主任 → 院长 → 校长
定义:避免请求发送者与接收者耦合,通过让多个对象都有机会处理该请求,将这些对象连成一条链,请求沿着链传递,直到有对象处理它
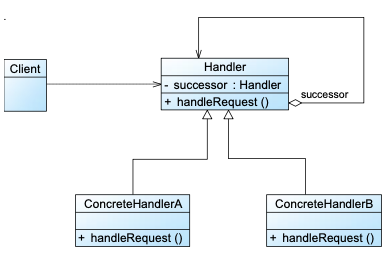
1 | |
“自己处理不了 → 交给下一个”
15. Command Pattern 命令模式 🌟🌟🌟🌟
动机:把“请求”封装成对象,使发送者与接收者完全解耦。
Intent:
- Encapsulate a request in an object (请求封装成对象)
- parameterization of clients with different requests (客户端可以随意组合不同命令)
- queue or log requestes (支持排队、日志、撤销)
定义:Encapsulate a request as an object… support undoable operations.
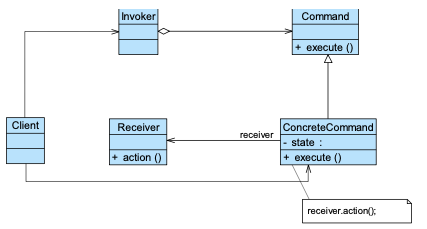
① Command 抽象类
1 | |
“How to execute should be implemented in receiver.”
② ConcreteCommand 实现类
1 | |
“‘继承’ 用来连接命令与接收者。execute 调用 receiver.action()”
③ Receiver
1 | |
“这里是真正执行操作的地方”
④ Invoker
1 | |
“Invoker 只负责执行 command,而不知道 command 如何实现”
优缺点
- Code scalable as we can add new commands without changing existing code
- Increase loose-coupling
- Increase in the number of classes
16. Iterator Pattern 迭代模式 🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟
动机:在不知道集合内部结构的前提下,一步一步访问其中的元素。
定义:Provides a method to access an aggregate object without exposing its internal structure.
类图
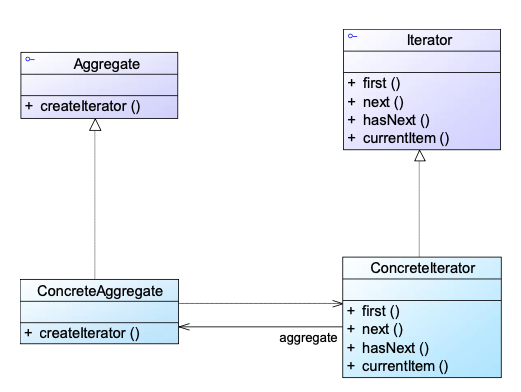
代码
1 | |
优缺点
- Support multiple traversal ways
- Simplify the aggregate class
- 符合Single Responsibility Principle
- 符合Open-Closed Principle
- 增加了大量的类
- 抽象迭代器设计难度大
20. Strategy Pattern 策略模式 🌟🌟🌟🌟
动机:同一个目标,可以根据不同环境选择不同策略。
定义:定义一系列算法,把每个算法封装起来,使它们可以互换。策略模式使算法可以独立于使用它的客户而变化。
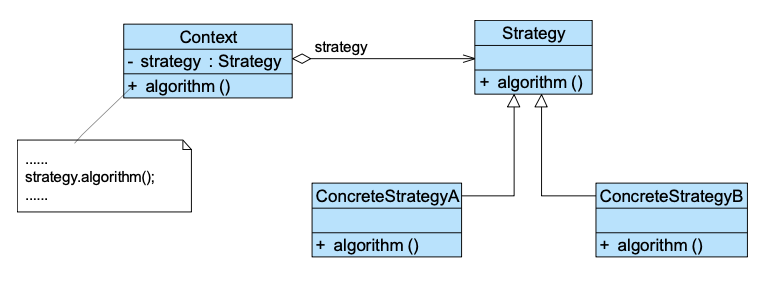
1 | |
优缺点
- 符合Open-Closed Principle
- Offer a way to manage related families of algorithm
- an alternative to inheritance relationships
- avoid multiple if-else
- Clients must know all the strateggy classes
- 策略类数量可能众多
- 一个Context无法同时使用多个策略
复习
三类设计模式,不考结构形和行为型中变灰色的和study by you self
选择 + 简答 + 应用
应用题考查创建型的行为模式
UML了解是可视化的建模工具,了解类图,类图的组成部分,如何绘制
依赖关系如何绘制,虚线实线
这些绘制的方法会用在具体的做题中,需要掌握如何使用
OO
七个设计原则和相对应的设计模式。设计模式符合哪个设计原则,开闭原则重点,里氏替换,LOD减少耦合
设计模式
- 简单工厂:看一下相关的例子,优缺点不展开了,比较细碎
- 工厂方法模式:解决简单工厂模式的问题,无法符合开闭原则。
- 抽象工厂模式:考虑了最多的唯独
- 建造者模式:Step-by-step
- 单例模式:单一实现,提供全局访问点
- 原型模式:浅克隆和深克隆
- 适配器模式:两种的区别的对应
- 桥接模式:如何用组合的方式替换继承的方式
- 装饰模式: